Setting achievable and impactful business goals is crucial for the success of any organization. Without clearly defined objectives, businesses can easily lose direction and fail to reach their full potential. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to set business goals that are not only achievable but also drive significant impact. We will explore the importance of setting SMART goals – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound – and discuss the process of developing goals that align with your overall business strategy. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, understanding how to set effective business goals is essential for sustained growth and success.
From defining your business objectives to tracking your progress and making necessary adjustments, this guide will cover all the key aspects of setting achievable and impactful goals. We will delve into the benefits of setting SMART goals, providing practical examples and actionable strategies you can implement immediately. Learn how to create business goals that motivate your team, improve performance, and ultimately contribute to the long-term success of your organization. Mastering the art of goal setting is a vital skill that empowers businesses to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth.
SMART Goal Framework Explained
The SMART framework provides a structured approach to goal setting, ensuring objectives are clear, attainable, and contribute meaningfully to overall success. Each element of the acronym represents a key characteristic of effective goals.
Specific: Goals should be clearly defined, avoiding vague language. What exactly needs to be accomplished?
Measurable: Progress must be quantifiable. How will success be measured? What metrics will be used?
Attainable: Goals should be challenging yet realistic, considering available resources and constraints. Is the goal achievable within the given timeframe and resources?
Relevant: Goals must align with the overall strategic objectives of the business. How does this goal contribute to the broader vision?
Time-Bound: A clear deadline or timeframe should be established. When must this goal be completed?
Aligning Goals with Vision and Values
Goal setting isn’t just about identifying desired outcomes; it’s about ensuring those outcomes propel your business in the right direction. This requires aligning your goals with your overarching vision and core values.
Your vision statement paints a picture of your desired future state. It provides the “why” behind your efforts. Goals should contribute to realizing this vision.
Values define the principles guiding your business conduct. Goals should be pursued in a manner consistent with these values. For example, if integrity is a core value, goals shouldn’t be achieved through unethical practices.
By aligning goals with vision and values, you create a sense of purpose and ensure your actions contribute to long-term, sustainable success.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Objectives
Understanding the difference between short-term and long-term objectives is crucial for effective goal setting. Short-term objectives are milestones achieved within a relatively short timeframe, typically less than a year. They act as stepping stones towards achieving larger goals.
Long-term objectives represent the overall, ultimate aspirations of your business, usually spanning several years or even a decade. These objectives define the desired future state of your organization and guide its overall direction. The interplay between these two types of objectives creates a roadmap for success.
Cascading Goals Across Departments

Once overarching business goals are established, it’s crucial to cascade them down to individual departments. This ensures everyone works towards a common objective, fostering alignment and maximizing impact.
Start by clearly defining how each department can contribute to the broader goals. This may involve breaking down high-level goals into smaller, department-specific objectives. Ensure these objectives are measurable and achievable within the department’s scope.
Transparency is key during this process. Communicate clearly with each department about their roles and responsibilities. Open communication facilitates collaboration and prevents silos, ensuring everyone understands how their work contributes to the bigger picture.
Tracking Progress with KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial for monitoring progress toward your business goals. They provide quantifiable metrics that demonstrate how effectively your strategies are performing.
Select KPIs that directly align with your defined objectives. For instance, if your goal is to increase brand awareness, relevant KPIs might include website traffic, social media engagement, or reach. If your aim is to improve customer retention, KPIs like customer churn rate or customer lifetime value are more appropriate.
Regularly review your KPIs to identify areas of strength and weakness. This consistent monitoring allows for timely adjustments and optimizations to your strategies, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your business goals.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Setting impactful business goals requires careful planning and execution. Avoid these common pitfalls to increase your chances of success.
Lack of Specificity
Vague goals lead to ambiguous outcomes. Ensure your goals are SMART – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Ignoring Resources
Consider available resources like budget, personnel, and time. Setting goals without considering limitations sets you up for failure.
Failing to Track Progress
Regularly monitor progress. Track key metrics to identify potential roadblocks early and adjust strategies as needed.
Using OKRs for Goal Management
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) offer a robust framework for managing and achieving goals. Objectives define what you want to accomplish. They should be qualitative, aspirational, and engaging. Key Results, on the other hand, specify how you’ll measure progress towards your objective. They should be quantitative, measurable, and time-bound.
OKRs promote alignment and focus by connecting high-level company objectives with individual team and employee contributions. This framework encourages transparency and accountability, as progress is regularly tracked and reviewed. OKRs also foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging ambitious goal setting and iterative learning.
Feedback Loops and Adjustments
Establishing effective feedback loops is crucial for monitoring progress towards your business goals. Regularly review your key performance indicators (KPIs) and assess whether your strategies are yielding the desired results.
Don’t be afraid to adjust your goals or methods if necessary. Market conditions, unforeseen challenges, or new opportunities may require you to adapt your initial plans. Flexibility is key to achieving long-term success. A dynamic approach allows you to stay on track and maximize your chances of achieving impactful outcomes.
Celebrating Milestones
Recognizing and celebrating milestones is crucial for maintaining motivation and momentum. It provides a sense of accomplishment and reinforces positive behaviors. This celebration doesn’t need to be extravagant; even small acknowledgements can be impactful.
Consider implementing a system for tracking progress and celebrating successes. This could involve:
- Regular team meetings to discuss achievements.
- Small rewards for reaching specific targets.
- Company-wide announcements of significant milestones.
By acknowledging accomplishments, you foster a culture of achievement and inspire continued progress towards larger goals.
Reviewing Goals Quarterly
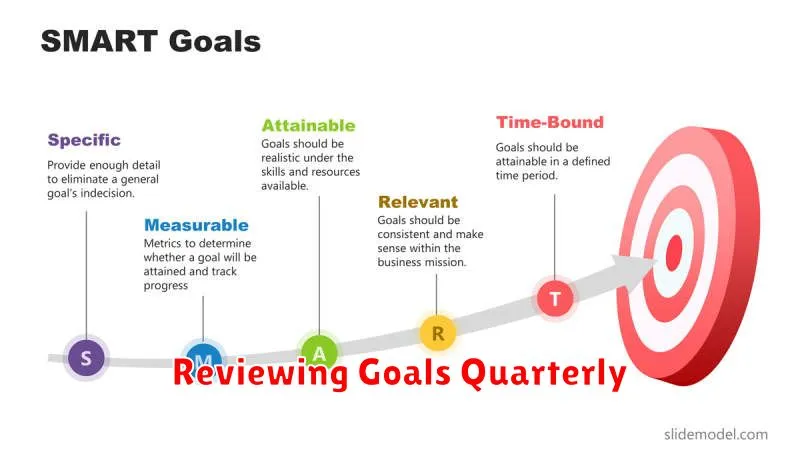
Quarterly reviews are essential for maintaining momentum and adapting to change. This frequency allows for adjustments before significant deviations occur. It also provides opportunities to celebrate successes and reinforce positive behaviors.
During these reviews, evaluate progress against key performance indicators (KPIs). Analyze what’s working, what’s not, and why. Based on this analysis, adjust strategies, reallocate resources, or revise targets as needed to stay on track.
Documentation is crucial. Record decisions made, revised plans, and any new insights gained during the review. This creates a valuable record of progress and provides context for future decisions.

