In today’s rapidly evolving economic landscape, building a sustainable business model is no longer a choice but a necessity. It requires a shift from traditional, short-term profit maximization to a more holistic approach that considers the environmental, social, and economic impacts of business operations. This article will explore the key elements of a sustainable business model, providing a comprehensive guide for organizations seeking to build resilience, enhance their brand reputation, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Understanding the principles of sustainability, incorporating sustainable practices, and measuring your sustainability performance are all crucial steps toward building a business model that thrives in the long term.
Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, embracing sustainability can unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation. From reducing waste and optimizing resource utilization to fostering ethical supply chains and engaging with stakeholders, the benefits of a sustainable business model are numerous. This article will equip you with practical strategies and actionable insights to effectively integrate sustainability into your core business strategy, enabling you to create a truly sustainable and prosperous future for your organization and the planet.
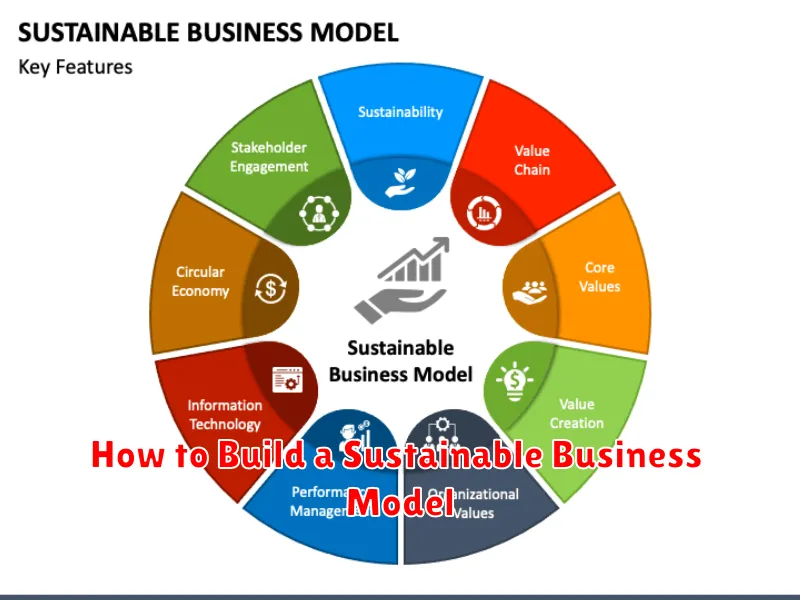
What Is a Sustainable Business Model?
A sustainable business model goes beyond traditional profit-driven approaches. It incorporates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into its core operations.
This means a company considers its impact on the planet, treats its employees and stakeholders fairly, and operates ethically and transparently. A sustainable model strives to create long-term value not just for shareholders, but for all stakeholders and the environment.
It focuses on reducing negative impacts while maximizing positive contributions. This could include minimizing waste, reducing emissions, promoting ethical sourcing, and investing in community development.
Balancing Profit with Purpose
A sustainable business model requires a delicate balance between generating profit and fulfilling a purpose. Profitability ensures the business can operate and grow, providing resources for investment and innovation. Purpose, on the other hand, provides the driving force, attracting customers and employees who align with the company’s values.
Finding this balance involves identifying a societal or environmental need that the business can address while simultaneously generating revenue. This can manifest in various ways, such as offering eco-friendly products, supporting ethical labor practices, or donating a portion of profits to a relevant cause.
Striking the right balance ensures long-term sustainability. Focusing solely on profit can lead to negative consequences, damaging reputation and alienating stakeholders. Conversely, prioritizing purpose without adequate profitability can lead to financial instability, hindering the business’s ability to achieve its goals.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction
A core principle of a sustainable business model is embracing the circular economy. This regenerative approach aims to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
Traditional linear models (take-make-dispose) contribute significantly to environmental problems. Circular models, in contrast, prioritize reducing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products. This creates closed-loop systems where waste is minimized and resources are kept in use for as long as possible.
Implementing circularity within your business model can involve strategies like designing products for durability and recyclability, incorporating recycled materials in production, and offering product take-back programs. These actions contribute to waste reduction at all stages of the product lifecycle, fostering a more sustainable and environmentally responsible operation.
Social Responsibility and Impact
A truly sustainable business model considers its social responsibility and impact. This involves understanding and mitigating any negative impacts of business operations while actively contributing to societal well-being. Ethical labor practices, fair wages, and safe working conditions are fundamental.
Beyond internal practices, consider the broader impact on the community and environment. Supporting local initiatives, minimizing pollution, and sourcing materials responsibly demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. This builds trust with consumers and stakeholders, enhancing the long-term sustainability of the business.
Energy Efficiency and Green Operations
Minimizing environmental impact is crucial for a sustainable business model. Energy efficiency plays a key role in achieving this.
Implement measures to reduce energy consumption across operations. This includes utilizing energy-efficient equipment, optimizing building design for natural light and ventilation, and implementing smart energy management systems.
Embrace green operations by reducing waste, promoting recycling, and sourcing sustainable materials. Consider adopting circular economy principles to minimize resource depletion and waste generation.
These efforts not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also often translate into cost savings, enhancing the overall business model.
Long-Term Financial Planning
Long-term financial planning is crucial for building a sustainable business model. It provides a roadmap for achieving financial stability and growth over an extended period, typically five to ten years or more. This planning involves forecasting future revenue and expenses, considering potential risks and opportunities, and establishing clear financial goals.
Key aspects of long-term financial planning include developing a comprehensive budget, establishing investment strategies, and creating a contingency plan for unexpected economic downturns. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan is essential to adapt to changing market conditions and ensure the business remains on track to achieve its long-term objectives.
Sustainability in Supply Chains
A sustainable supply chain minimizes negative environmental and social impacts while maintaining economic viability. This involves scrutinizing every stage, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing, distribution, and end-of-life management.
Key aspects include responsible sourcing of materials, reducing emissions throughout the supply chain, promoting fair labor practices, and minimizing waste.
Implementing sustainable practices in your supply chain can lead to cost savings through improved efficiency, enhanced brand reputation, and reduced regulatory risks.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethics
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of building a sustainable business model. Adhering to relevant laws and regulations not only avoids penalties and legal issues but also builds trust with stakeholders.
Equally important is a strong ethical foundation. Businesses must operate with integrity, fairness, and transparency. This includes considering the environmental and social impact of business decisions. A commitment to ethical practices enhances reputation and fosters long-term sustainability.
Metrics to Measure Sustainability
Measuring sustainability performance involves tracking key metrics across various aspects of your business. This provides quantifiable data to assess progress and identify areas for improvement. Environmental metrics often include greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and waste generation. Tracking these helps understand your environmental footprint.
Social metrics focus on the impact your business has on people, both internally and externally. These can include employee satisfaction, fair labor practices, community engagement, and product safety. Measuring social impact ensures ethical operations and positive contributions to society.
Economic sustainability metrics assess the long-term financial viability of your business model while considering environmental and social factors. These may include resource efficiency, operating costs, and supply chain resilience. Analyzing these aspects contributes to responsible financial performance.
Success Stories of Sustainable Brands

Examining successful sustainable businesses provides valuable insights. Patagonia, known for its commitment to environmentalism, has built a loyal customer base by prioritizing recycled materials and advocating for responsible manufacturing. Their success demonstrates the power of transparency and genuine commitment.
Another example is Tesla. While primarily focused on technological innovation, Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy has resonated strongly with consumers. This demonstrates how sustainability can be a core driver of market disruption and brand differentiation.
Interface, a flooring company, has achieved impressive sustainability milestones through its “Mission Zero” initiative, aiming to eliminate any negative impact on the environment. Their focus on closed-loop manufacturing and renewable energy showcases how sustainability can drive innovation and operational efficiency.