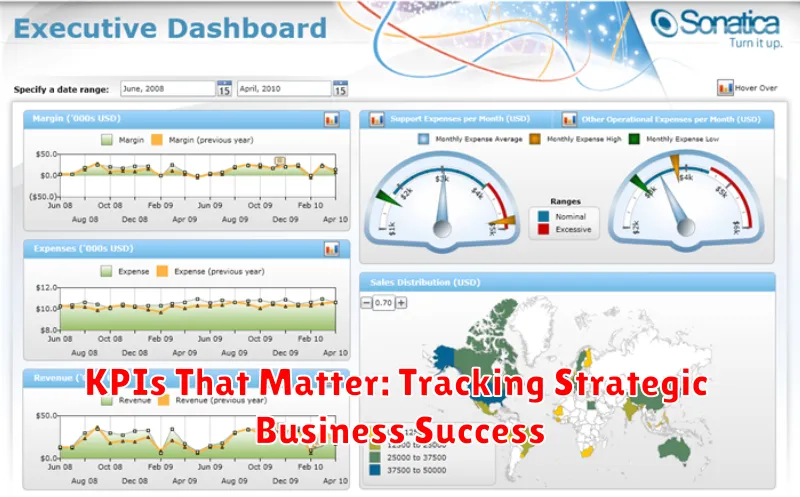
In today’s dynamic business landscape, tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is paramount to achieving strategic business success. KPIs provide quantifiable measurements of progress towards pre-defined objectives, offering invaluable insights into the effectiveness of business strategies. By diligently monitoring the right KPIs, organizations can identify areas of strength, pinpoint weaknesses, and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance and drive business growth. This article will explore the most critical KPIs that matter, providing a framework for businesses to effectively track and measure their journey towards achieving strategic success.
Selecting and tracking the appropriate KPIs is essential for businesses seeking to achieve strategic business success. Focusing on vanity metrics or overlooking crucial performance indicators can lead to misguided strategies and hinder growth. This article will delve into the KPIs that matter most, categorized by key business areas such as finance, marketing, sales, and customer satisfaction. By understanding and leveraging these key performance indicators, organizations can gain a comprehensive view of their performance, make informed decisions, and ensure they are on the right track to realizing their strategic business objectives.
What Are KPIs and Why They Matter
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable measurements used to evaluate the success of an organization, employee, or project in meeting strategic and operational goals. They provide a focused view of performance and help track progress toward desired outcomes.
KPIs matter because they provide objective evidence of progress, identify areas needing improvement, and inform strategic decision-making. By tracking KPIs, organizations can align their activities with strategic objectives and ensure they are moving in the right direction.
Strategic vs Operational KPIs
Understanding the difference between strategic and operational KPIs is crucial for effective performance management. Strategic KPIs provide a high-level view of progress towards long-term organizational goals. They focus on overall performance and are typically monitored by executive leadership. Examples include market share, customer lifetime value, and return on investment.
Operational KPIs, on the other hand, measure the efficiency and effectiveness of day-to-day activities within specific departments or functions. They offer a granular perspective on performance and inform operational decisions. Examples include production output, customer satisfaction scores, and sales conversion rates. Operational KPIs contribute to the achievement of strategic objectives.
Choosing the Right KPIs for Your Business
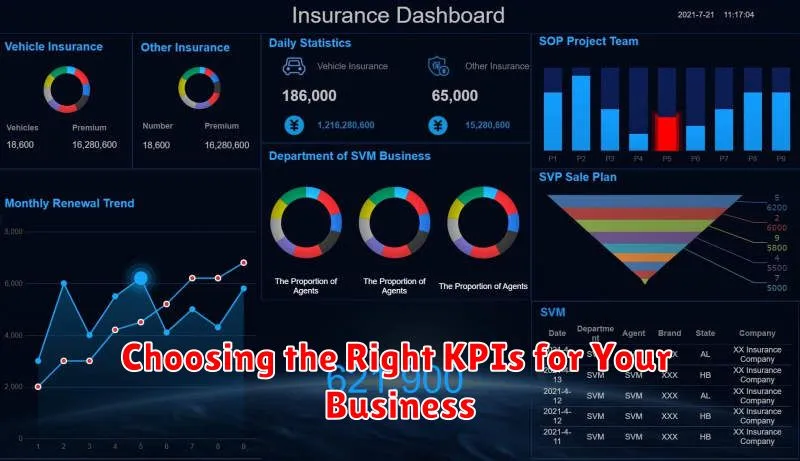
Selecting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for effective business management. KPIs provide quantifiable measurements of progress towards strategic objectives. The wrong KPIs can lead to misdirected efforts and wasted resources.
Consider your specific business goals. Are you focused on increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction, or streamlining operations? Each goal requires different KPIs.
For example, if your goal is to increase revenue, relevant KPIs might include average order value or customer lifetime value. If customer satisfaction is paramount, consider tracking metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer churn rate.
Choose KPIs that are measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. Regularly review and adjust your KPIs as your business evolves.
Customer-Focused Metrics
Customer-focused metrics provide crucial insights into customer behavior and satisfaction, driving business growth and loyalty. These metrics help businesses understand customer needs and pain points, enabling them to improve products, services, and the overall customer experience.
Key metrics include Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), which measures happiness with specific interactions, Net Promoter Score (NPS), which gauges the likelihood of recommendations, and Customer Churn Rate, indicating the percentage of customers lost over a given period. Monitoring these metrics allows for data-driven decisions that enhance customer relationships and contribute to long-term success.
Financial Performance Indicators
Financial KPIs provide insights into the monetary health and stability of a business. They are crucial for understanding profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
Key financial performance indicators include:
- Revenue: The total income generated from sales.
- Profit Margin: The percentage of revenue remaining after deducting expenses.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Indicates the proportion of company financing that comes from debt versus equity.
- Current Ratio: A liquidity ratio that measures a company’s ability to pay short-term obligations.
Tracking these KPIs allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, make informed decisions, and ensure long-term financial sustainability.
Employee Engagement and Productivity
Employee engagement is a crucial driver of productivity and overall business success. Engaged employees are more likely to be invested in their work, leading to increased output and higher quality results.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) related to engagement often include metrics like employee satisfaction, retention rates, and absenteeism. Tracking these metrics can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the workforce.
Productivity KPIs can be measured through various methods, including output per employee, revenue generated per employee, or project completion rates. By monitoring productivity alongside engagement, businesses can identify correlations and implement strategies for improvement.
Growth and Market Penetration KPIs
Growth and market penetration KPIs provide crucial insights into a company’s success in expanding its reach and capturing a larger market share. These metrics help businesses understand their growth trajectory and effectiveness in penetrating target markets.
Key performance indicators in this category often include:
- Market Share: Percentage of the total market controlled by the company.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost associated with acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted total revenue generated by a customer throughout their relationship with the company.
- Revenue Growth Rate: The rate at which a company’s revenue increases over time.
Tracking these KPIs allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, optimize marketing strategies, and ultimately drive sustainable growth and market dominance.
Setting Targets and Benchmarks
Establishing effective Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) requires careful consideration of targets and benchmarks. Targets represent the desired level of performance for a given KPI. They should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART).
Benchmarks provide context for evaluating KPI performance. Internal benchmarks compare performance against past results or across different departments within the organization. External benchmarks compare performance against competitors or industry averages. By analyzing performance against both targets and benchmarks, businesses can gain valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
Dashboard Tools for KPI Tracking
Selecting the right dashboard tool is crucial for effective KPI tracking. A robust dashboard provides a centralized view of your key performance indicators, allowing for real-time monitoring and informed decision-making.
Several popular dashboard tools offer varying features and functionalities. Some focus on data visualization, while others specialize in integrations with various data sources. Consider factors such as your budget, technical expertise, and specific reporting needs when choosing a tool.
Key features to look for include customizable dashboards, automated reporting, and alerting capabilities. These features streamline the tracking process and ensure you’re promptly notified of any significant changes in your KPIs.
How to Analyze and Act on KPI Data
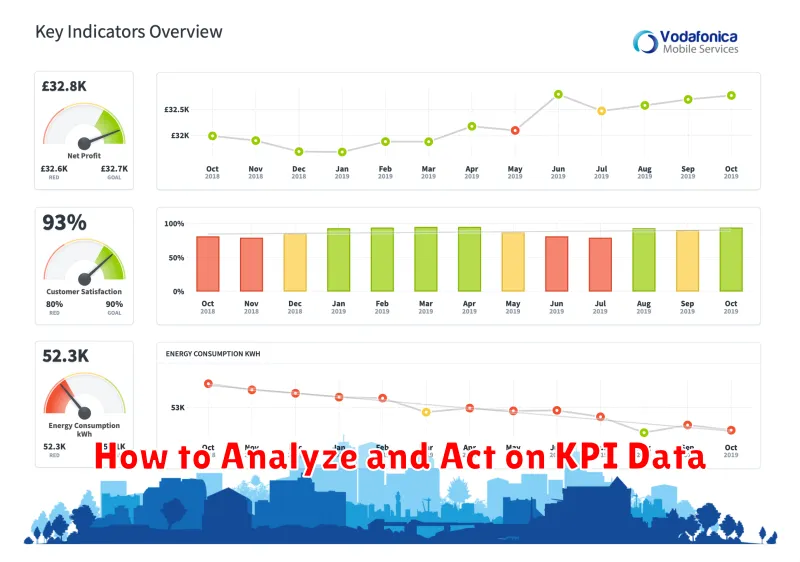
Analyzing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) involves a systematic approach to understanding their trends and implications. Begin by regularly collecting and compiling your KPI data. Then, compare current performance against historical data and pre-defined targets to identify areas of strength and weakness.
Look for patterns and trends to understand the underlying causes of performance fluctuations. This analysis should inform strategic decision-making. Based on your insights, take corrective actions to improve underperforming areas and capitalize on successful strategies. This might involve adjusting resource allocation, refining processes, or implementing new initiatives.
Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure your actions are yielding the desired results and to adapt your strategies as needed.