In today’s fiercely competitive market landscape, understanding and implementing effective pricing strategies is paramount to success. Pricing isn’t simply about attaching a number to your product or service; it’s a complex interplay of factors influencing customer perception, profit margins, and market share. This article delves into the fundamentals of pricing strategy, providing a framework for businesses to navigate the challenges of competitive markets. Whether you’re launching a new product, reevaluating your current pricing model, or seeking to optimize your pricing strategy for maximum profitability, understanding these core principles is crucial. Mastering the art of competitive pricing can be the key differentiator between thriving and merely surviving in the modern business environment.
We will explore the various pricing strategies available, ranging from cost-plus pricing and value-based pricing to competitive pricing and premium pricing. We’ll analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, helping you identify the optimal pricing strategy for your specific business needs. Furthermore, we’ll discuss the importance of market research, competitor analysis, and understanding customer price sensitivity in developing a robust and effective pricing strategy for competitive markets. This foundational knowledge will empower you to make informed pricing decisions that drive revenue growth and strengthen your competitive position.
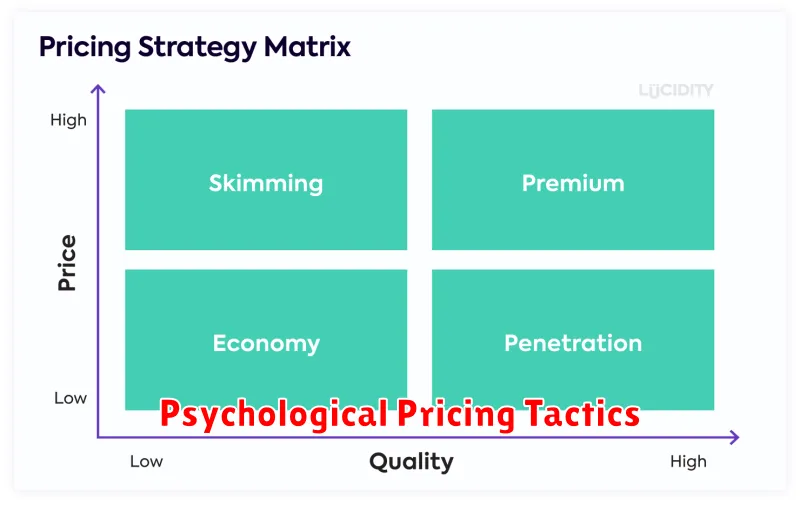
Different Pricing Models Explained
Pricing models are frameworks businesses use to determine the optimal price for their products or services. Choosing the right model is crucial for profitability and market competitiveness.
Cost-plus pricing involves adding a fixed percentage markup to the cost of production. This ensures a profit margin but doesn’t consider market dynamics.
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value offered to the customer. This model prioritizes understanding customer needs and willingness to pay.
Competitive pricing benchmarks prices against competitors. This strategy can be effective in established markets but may lead to price wars.
Understanding Cost-Based vs. Value-Based Pricing
Two fundamental pricing strategies exist: cost-based and value-based. Cost-based pricing calculates the selling price by adding a markup to the cost of production. This ensures profitability but may not align with market value. It’s simpler to implement but can be less effective in competitive markets.
Value-based pricing, conversely, sets prices based on the perceived value a product offers to the customer. This strategy focuses on customer willingness to pay, allowing for potentially higher profits. While more complex to determine, it’s often more effective in differentiated markets. Choosing the right strategy depends on your market, industry, and competitive landscape.
Analyzing Market and Competitor Pricing
A crucial aspect of pricing strategy involves a thorough analysis of both the market and competitor pricing. Understanding the prevailing market prices provides a baseline for your own pricing decisions. It helps identify the acceptable price range for your products or services within the current market landscape.
Competitor analysis is equally important. By examining your competitors’ pricing strategies, you can gain insights into their positioning and target market. This information can help you differentiate your offerings and determine whether to price above, below, or at parity with the competition. Knowing your competitors’ pricing allows you to anticipate their reactions to your pricing changes and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Psychological Pricing Tactics
Psychological pricing leverages consumer behavior to influence purchase decisions. These tactics often involve manipulating price points to create a perceived value or urgency.
Charm pricing, a common tactic, uses prices ending in .99 to suggest a bargain. For instance, $9.99 appears significantly cheaper than $10.00, even though the difference is negligible.
Prestige pricing uses higher price points to signal quality and exclusivity. Luxury brands often employ this tactic to attract status-conscious consumers.
Freemium and Subscription Models
Freemium models offer a basic service for free, enticing users to upgrade to a premium version with advanced features for a fee. This model relies on a large user base, converting a small percentage to paying customers. Key considerations include a compelling premium offering and effective conversion strategies.
Subscription models provide access to a product or service for a recurring fee, typically monthly or annually. This creates predictable revenue streams and fosters customer loyalty. Success depends on providing consistent value and managing churn rates.
Discounts, Bundles, and Limited Offers
Discounts, bundles, and limited-time offers are powerful tools for attracting customers and driving sales. They create a sense of urgency and value.
Discounts can include percentage or fixed amount reductions. Bundling involves combining products or services at a reduced overall price. Limited-time offers create scarcity, encouraging immediate purchase.
These tactics can be used strategically to clear out excess inventory, introduce new products, or reward loyal customers.
Dynamic and Real-Time Pricing
Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing or time-based pricing, involves adjusting prices flexibly based on various market factors. These factors can include demand fluctuations, competitor pricing, and even real-time events.
Real-time pricing takes this concept a step further by continuously analyzing market data and immediately reflecting price changes. This approach is particularly relevant in fast-paced markets like online retail, travel, and hospitality.
Benefits of dynamic and real-time pricing include optimized revenue generation, improved responsiveness to market shifts, and better inventory management.
However, challenges exist such as potential customer dissatisfaction if price changes are perceived as unfair or manipulative, and the need for sophisticated technological infrastructure to support these strategies.
Tracking Profit Margins and KPIs
Profit margin monitoring is crucial for evaluating pricing strategy effectiveness. Regularly track gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin to understand the impact of pricing decisions on profitability.
Beyond profit margins, key performance indicators (KPIs) provide deeper insights. Track metrics like customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and market share to gauge the overall success of your pricing strategy in the competitive landscape.
Analyzing these metrics together provides a comprehensive view, allowing for data-driven adjustments to pricing strategies and optimizing for long-term profitability.
Testing and Adjusting Pricing
Testing your pricing strategy is crucial for maximizing revenue and maintaining competitiveness. A/B testing different price points allows you to observe consumer behavior and identify optimal pricing levels. Analyze sales data, conversion rates, and customer feedback during testing periods. This provides valuable insights into price sensitivity and helps determine which price points resonate best with your target audience.
Adjusting prices is an ongoing process. Market conditions, competitor actions, and seasonality can impact the effectiveness of your pricing strategy. Regularly review and refine your pricing to ensure it aligns with current market dynamics and business objectives. Don’t be afraid to incrementally increase or decrease prices based on market response and internal cost factors.
Examples from Top Companies
Examining pricing strategies of successful companies offers valuable insights. Netflix utilizes a value-based pricing model, offering tiered subscriptions with increasing features and benefits. This caters to varying customer needs and budgets, maximizing market penetration.
Costco’s membership-based model creates customer loyalty and predictable revenue streams, allowing them to offer competitively priced products. Their focus on cost leadership enables them to maintain low prices while generating profits through membership fees.
Apple often employs a premium pricing strategy, positioning their products as high-quality and innovative. This strategy targets a specific customer segment willing to pay more for perceived value and brand prestige.

